User Research: Seven Steps to Master User Research
Introduction
With the change of times and the development of business, the market form has evolved from the original seller's market to a buyer's market where users decide everything.
The importance of users to business has been increasingly perceived by enterprises, and user research in enterprises has also received more and more attention.
The enterprises here include traditional enterprises, such as real estate industry, automobile industry, FMCG industry, supermarket industry, durable consumer goods industry, etc., as well as emerging Internet enterprises and enterprises in new consumption fields.
This article aims to combine my many years of work experience in the field of user research with the work rhythm and mode of "running in small steps" for user research work in the Internet field, and try to extract and form a set of agile user research project methodology suitable for the Internet or new consumption fields.
The framework of this methodology is mainly composed of seven core steps, so it is called seven steps of user research. The specific steps are shown in the figure below:

1. Clear goals & pull together cognition
Usually, a user research project in an enterprise will include the business department that proposes the demand and the user research department that undertakes the work.
The interior of each department is composed of personnel with different levels or different responsibilities, so the core key before a research project is to pull together cognition.
Clarify the action plan, including the understanding and identification of background and objectives, the confirmation of specific research methods and research contents, the evaluation and identification of time and cost, the expected output, the division of responsibilities of personnel, etc.
Therefore, before the project starts, all the above-mentioned cognitions that need to be aligned need to be reflected in the standard content that can be shared and referenced in the process. This is the project proposal.
Overall, the project proposal includes:
- Project background research;
- Project research objectives;
- Disassembly of research ideas and research contents based on research objectives;
- The research method and implementation plan set according to the research idea and research content;
- Time planning and budget evaluation;
- Staff responsibilities.
At this stage, a directional framework must be determined, such as the specific research content, specific research methods (qualitative research/quantitative research?), and specific implementation methods under the research methods (forum/in-depth interview? Street visit/online Questionnaire?) Specific sample design conditions (coverage area, city, specific sample conditions, etc.).
2. Confirmation of research types and methods
Strictly speaking, this step is not a process link of the user research project, but a research method that runs through the entire user research project process.
However, because this step is the core basic cognition to understand the user methodology and complete the user research project, we set it as a separate step to elaborate the qualitative and quantitative core methodologies of specific traditional field research.
The types of research can be divided into qualitative research and quantitative research. Qualitative research is a logical analysis of causes, which has the characteristics of exploration, diagnosis and prediction.
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research is an in-depth and open research on the process, attitude and motivation of decision-making. Its technology comes from psychology, sociology and anthropology.
Common research methods include FGD focus group discussions, IDI in-depth interviews, Ethnography, Shop-Along escort activities, and Workshop creative workshops.
However, qualitative research also has many shortcomings:
Non quantifiable (no statistical significance), cannot be inferred to the whole (small sample, strong description, but no data support), personal feeling is greater than rational judgment, and cannot be used as a decision alone.

2. Quantitative research

3. Sampling and quota
1. Probability Sampling and Non-Probability Sampling
Due to efficiency and practical considerations, it is difficult for us to conduct research on all target users.
This requires us to carry out sample quotas and sampling, and the sampling methods can be divided into probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
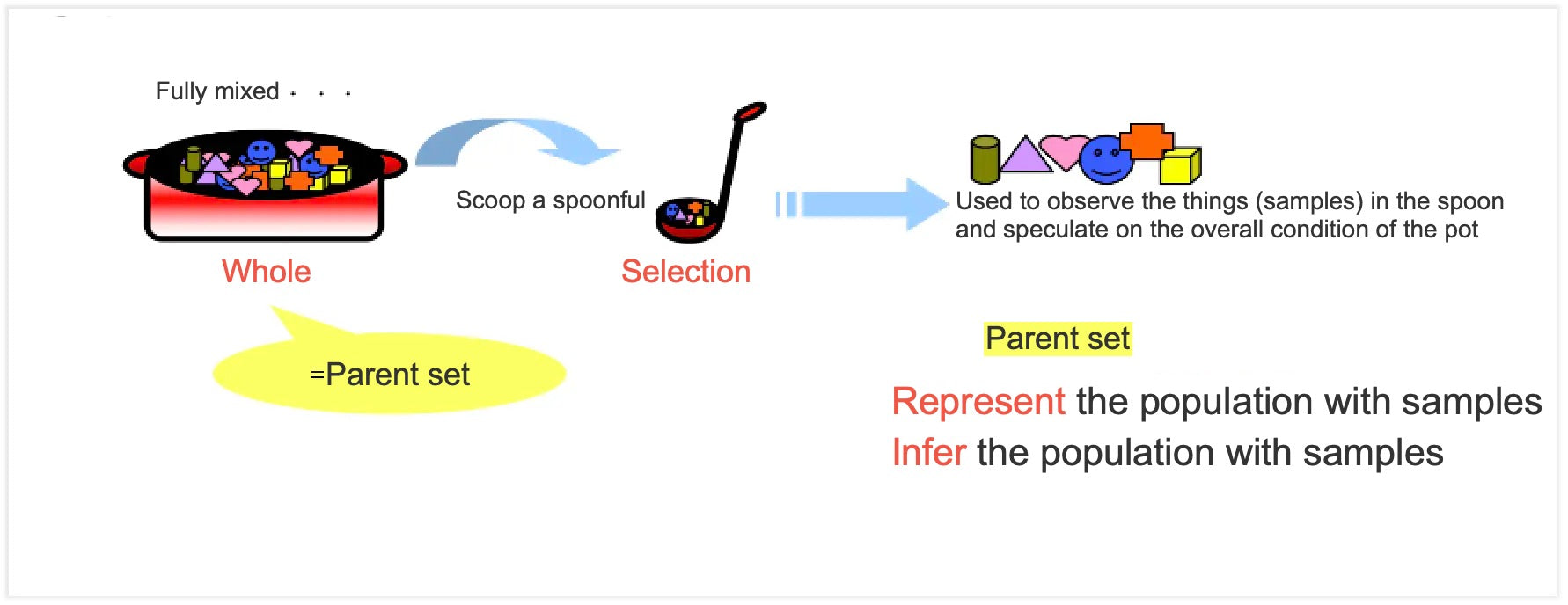
Probability sampling refers to that the probability of each user being drawn is the same, and the composition of the sample is basically consistent with the overall composition.
The population (which also has such regularity/propensity) can be inferred from the sample (regularity/propensity).
Non-probability sampling means that users, as individuals, have different probability of being drawn, and the composition of the sample is not completely consistent with the composition of the population, and the population cannot be inferred from the sample.
However, it can have a certain degree of representativeness, and can focus on the research target user groups (such as "urban female workers").
2. Quota Standard
Generally, in quantitative research, the sample size of each "analysis unit" is > = 100, and 30 samples have analytical significance.
In qualitative research, a sample size >=8 is considered to have research value and significance.
4. User identification
1. What characteristics of users does this study focus on?
Gender, age, educational background, marriage and childbirth, behavioral characteristics of using the company's products, potential users or users of competitive products.
The other category is people who are very familiar with research methods, such as practitioners in research companies/public relations/media-related industries and their families.
Other conditions, such as poor expression ability and low willingness to cooperate.
5. Preparation of qualitative interview outline and quantitative questionnaire

Structure of interview outline
Taking the office user demand insight project as an example, generally, the qualitative interview outline is divided into the following five structures:
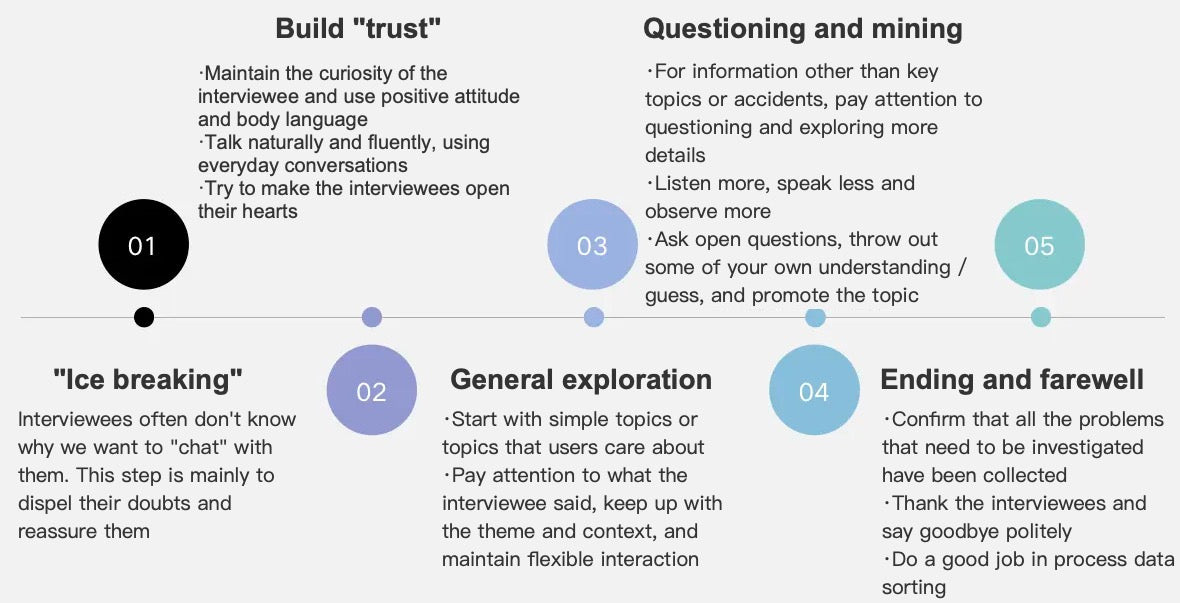
- Break the ice and clarify the rules of the game to users: clarify the purpose, explain the rules, and eliminate concerns;
- User Insights: Dig deep into the typical characteristics of target users from the aspects of lifestyle, values, leisure and entertainment, consumption concept, social type, brand preference, etc.;
- Pan office behavior and needs: daily social, work social and other related habits and tools, work type, rhythm, office environment, etc;
- Office behavior / scene / pain points and needs: office scene, use behavior under the scene, functional and emotional needs, use tools, specific feedback and evaluation, use pain points and future needs;
- Media habits: daily attention to information and information acquisition channels.
2. Principles of quantitative questionnaire
Usually, the quantitative questionnaire will cover the following parts. In the actual operation process, it can be flexibly established according to the subject to be studied:
- Sociological characteristics: sociological characteristics, marital status, brand usage, etc.;
- Usage behavior and evaluation: specific usage frequency, regularity, scene and evaluation, etc.;
- Product demand feedback: functional demand and emotional demand;
- Judgment of values statement: determine that users belong to a certain group;
- Leisure, entertainment and social networking;
- Consumption habits;
- Media habits.
6. Introduction to interview execution skills
1. Main stages, links and concerns of the interview
1. Important inquiry skills
- Make sure you are very familiar with the outline, do not completely separate from the outline, and do not be bound by the outline.
- When you hear what you think is important, follow them further, even if it means temporarily "out of writing".
- Focus on what the interviewee says and be prepared to dig deep at all times.
- Use reflective questions to confirm what you think you heard, such as "is that what you mean" and "you seem unhappy with...".
- Listen more, talk less, listen twice as long as you talk.
- From general to specific, from large to small.
- Remember that the most important question you can ask is "why?"
- Silence for a few seconds, let the respondents collect ideas and encourage them to share more information.
- Don't ask guiding questions, you will get the answer you expect!
- Don't argue with users or try to convince users.
- Do not ask questions repeatedly, each question can only be answered once.
- About: "Tell me more about...", "What do you think about...", "What do you think about...?"
- Accuracy: get more accurate information, such as "how to accurately describe your feelings...", "what does this compare to?", "What exactly do you mean?"
- Suppose: "what would you do if...?"
- Explore facts and details: e.g. "Why did you choose it? What needs did it meet for you".
- Open-ended: Use open-ended questions with many possible answers, not just "yes" or "no."
3. Other precautions
- Don't be late!
- Dress comfortably and casually. Don't wear exposed or fancy clothes, and don't wear too shabby.
- No ties, no heavy makeup, no perfume, no exaggerated jewelry.
- Don't reveal where you're from, don't have a company logo on your clothes, bags, pens, or notebooks to avoid bias.
- With the help of certain projection techniques.
7. Project output and report writing
The report process output methods show a trend of diversification, such as the traditional PPT format report, the EXCEL format data report, the Word format briefing report, and even the new online cloud document format report.
As Internet companies' demands for the efficiency of outputs are higher than the formal requirements, the final project output may not need a specific way of presentation, but just some "materials".
Therefore, the output of the report will not be repeated here, but only a brief overview of the output of the project from the process:
1. Quantitative reporting process

2. Qualitative reporting process
That's all. If you have any questions and suggestions, please leave a message.
If you like the article, please share it with others with page link, thanks for your supporting! ❤







































Leave a comment