Summary of Business Product Demand Management Methods
Introduction
Demands are the foundation of product design work, and that's where many practitioners get started. Demands runs through the whole process of product work, starting from business demand, and finally converting to the technical development demands of PRD, and the processing of demand in the middle is the deepening of demand. This article elaborates on the demands.
1. The source of demand
There are various sources of demand, and multiple demands are gathered together to form a demand list. The following is an analysis of the demand sources.
1) User appeal
It generally refers to the demands of end users. If it is a consumer product, then the demands fed back by users are demands. If it is a Business product, then you need to pay attention that the people who use the product may be diverse, such as company employees, managers, etc., and there may also be feedback from the business product which service consumer, but it should be noted that , the Business product feedback port may be collected uniformly by the informatization department of the enterprise.
2) Frontline department
Frontline departments undertake the functions of customer service, such as customer team, sales team, delivery team, after-sales team, etc. They must collect a large number of customer service situations in the service, and can put forward targeted optimization suggestions based on the current situation.
It should be noted that they may be limited by their own positions to view from their own perspective.
3) Leader's demands
Leader's demands may be the most nerve-wracking situation for everyone in daily work. It may be a few words in many cases, but it is a high priority.
General leadership demands can be understood as business demands, that is, leaders start from the current situation of the company's development and analyze which capabilities need to be expanded from the perspective of market layout, or what adjustments need to be made from the perspective of financing.
There is also a possibility that the boss greets the leader, that is, a political mission.
4) Product department
This kind of demand can mainly reflect the value of the product. It is necessary to analyze the user scenario and business status, combined with market research and judgment, to obtain high demand value.
If you just simply undertake the demands put forward by the business department and cannot analyze effective demands by yourself, then you can only act as a feature product manager, that is, you cannot use your effective product expertise to bring greater value to the enterprise.
5) Technical department
The source of such demands should not be underestimated. Generally, the code optimization demands proposed by the technical department from the perspectives of performance and code maintenance only need to be recorded and placed in the iteration table as planned.2. Demand management
There are various sources of demand. In order to effectively manage the demand, we need to have the correct management method. At the same time, we need to have different response strategies for different types of demand, which are explained below.
1. Product backlog management
After different demands are collected, they need to be under unified control. They can be maintained, followed up and tracked in a unified way. Associated demands can be consolidated, and life cycle management can be carried out for demands. Generally, tables are mainly used for maintenance, as shown in the following table:

The example fields in the table are the conventional fields that the author suggest, and you can add or subtract them. The explanation of each field is as follows:
- Demand name: an abstract summary after a brief description of the feedback requirement, such as adding a time filter item to a work order (requirement definition).
- Demand description: mainly describe what problems the user may encounter in what scenarios, and what the business process is like (business scenarios).
- Feedback source: it mainly records the category of the above sources.
- Feedback by: The main record person.
- Feedback time: Record the feedback time in time, and don’t delay too long.
- Status: generally pending, under judgment, rejected, in process, processed
- Followed-up by: who is handling it internally, as the person responsible for continuous follow-up
- Handling opinions: After internal discussion, it can be synchronized to the feedback person. The general feedback is as follows: feedback has been received before, feedback has been processed recently, feedback suggestions are unreasonable and attach reasons. If it is unreasonable, there may be unreasonable now but may be reasonable as circumstances changed.
This table mainly records the original demands of users, and strives to restore the usage scenarios of users under different services. It mainly describes business problems (or demands), and avoids recording modification suggestions for business staff. Among them, too few fields are not enough to fully express the demand itself and the management process, and too many fields are not easy to maintain, and it is easy to conflict with the other management tables, such as the demands research and development tracking table.
2. Maintenance mechanism
The demands placed in the product backlog need to be maintained regularly to avoid the situation of only collecting without feedback. Generally speaking, the main measures are as follows:
- Set up a special person to view the maintenance table and update it in time
- Check regularly, such as every Monday, check and update in time.
- Temporary spot checks, managers should temporarily spot check to drive regular maintenance
3. Tools
If you use the form to record and maintain, it may change over time, and the accumulation may be too large, which is inconvenient to handle. Therefore, it is recommended to use online tools for maintenance and use.
3. Demand value
For demands from different sources, after unified maintenance is performed in the product backlog table, value judgments and priorities maintenance are required. Demand can be judged according to the steps of demand analysis, quantitative judgment, priority setting, and execution plan.
1. Demand analysis
After receiving the demand, it is necessary to analyze the demand, mainly to judge its authenticity and its value. You can think about who will do what in what situation and for what purpose, and judge that it is a real situation, that is, it is valuable.
The 5W2H method can be used here to analyze:
- WHAT - what is it? What is the purpose? What to do?
- WHY - why do it? Can you not do it? Is there an alternative?
- WHO - who will do it?
- WHEN - what time to do it? When is the best time?
- WHERE - where to do it?
- HOW - how to do it? How to improve efficiency? How to implement? What is the method?
- HOW MUCH - to what extent? How's the quantity? What is the quality level? What is the input and output?
The first judgment is whether it is worthwhile.
2. Quantitative judgment
After qualitative analysis of demands, we have basically locked in valuable demands, but the size of the value still needs to be judged. Therefore, the multidimensional analysis method can be used for calculation.
First of all, we define multiple dimensions. For the Business product demands, we can use such as the user's willingness to pay, the user's pain level, the size of the audience, etc. to judge, and even to consider the cost, we can add the difficulty of implementation.
After comparing and scoring multiple dimensions of multiple demands, you can perform calculations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division to obtain judgment values, which can be used for quantitative analysis, and even combined with the company's strategic direction, you can weight the dimensions considered before performing quantitative analysis.
Name Explanation: The user's willingness to pay (if the user's willingness to pay for this service is high,the market will be broader), the user's degree of pain (the user's degree of pain for this problem is high, it is very inconvenient to not have this thing), the size of the audience (the larger the user or audience size, the greater the amount sold).
3. Prioritize
After quantitative analysis, we found out the demand for high value. However, when a demand is implemented, it will be disassembled into multiple small demands for implementation. So how can we judge its priority? We can use KANO analysis.
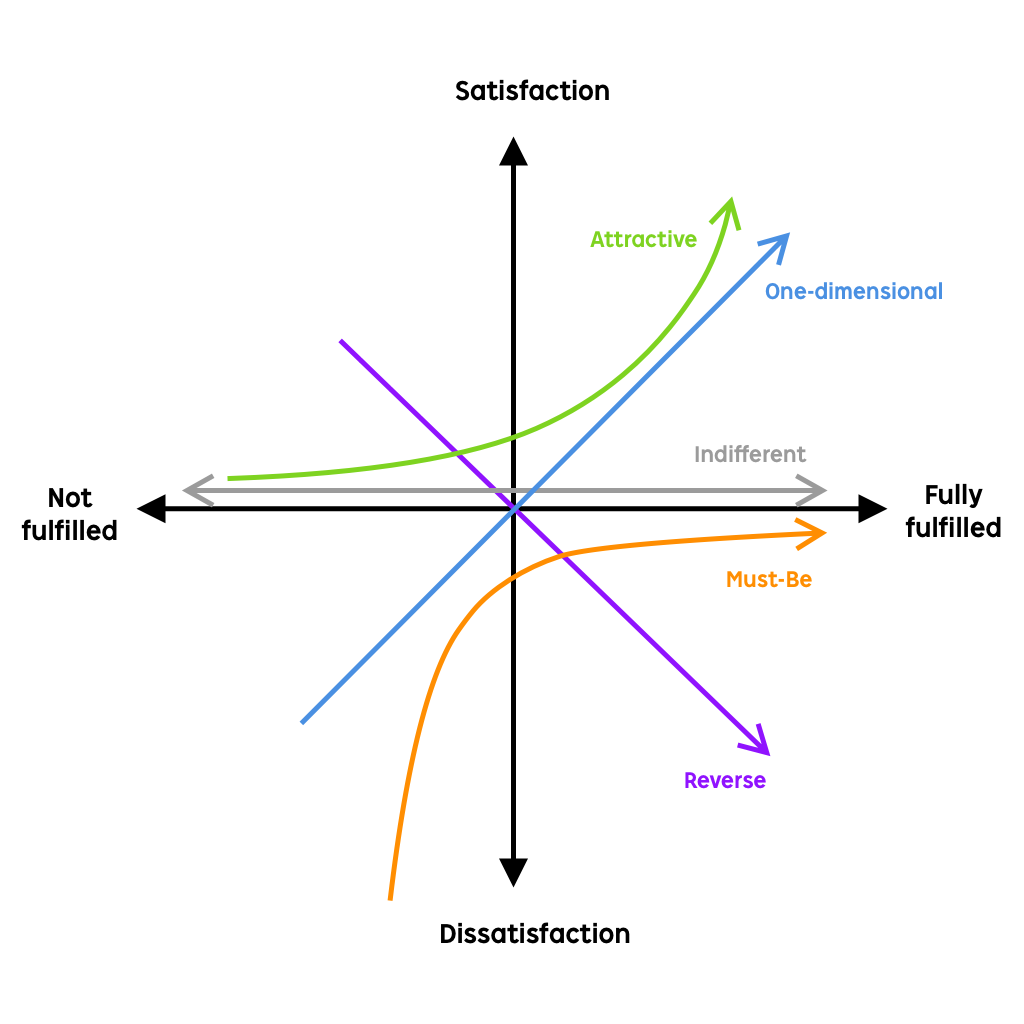
- Threshold Attributes (Basics) (Must-have features) – these are features that customers expect the service or product to have, these aren’t features that would necessarily impress customers but can cause dissatisfaction is missing.
- Performance Attributes (Satisfiers) (One-Dimensional features) – these features don’t come with the deal, rather add to the enjoyment level.
- Excitement Attributes (Delighters) (Attractive features) – these are the crucial features that increase the product/service’s competitors edge. This is the attribute to focus on as it will put you on a pedestal among your competitors.
- Indifferent Attributes – these are features that customers cannot decide if they are good or bad.
- Reverse Attributes – these features can be high quality or performance, but not increase satisfaction levels.
So it can be sorted as: Threshold Attributes > Performance Attributes > Excitement Attributes > Indifference Attribute > Reverse Attribute, of course, if it is indifference or reverse, it can basically be excluded.
4. Execution plan
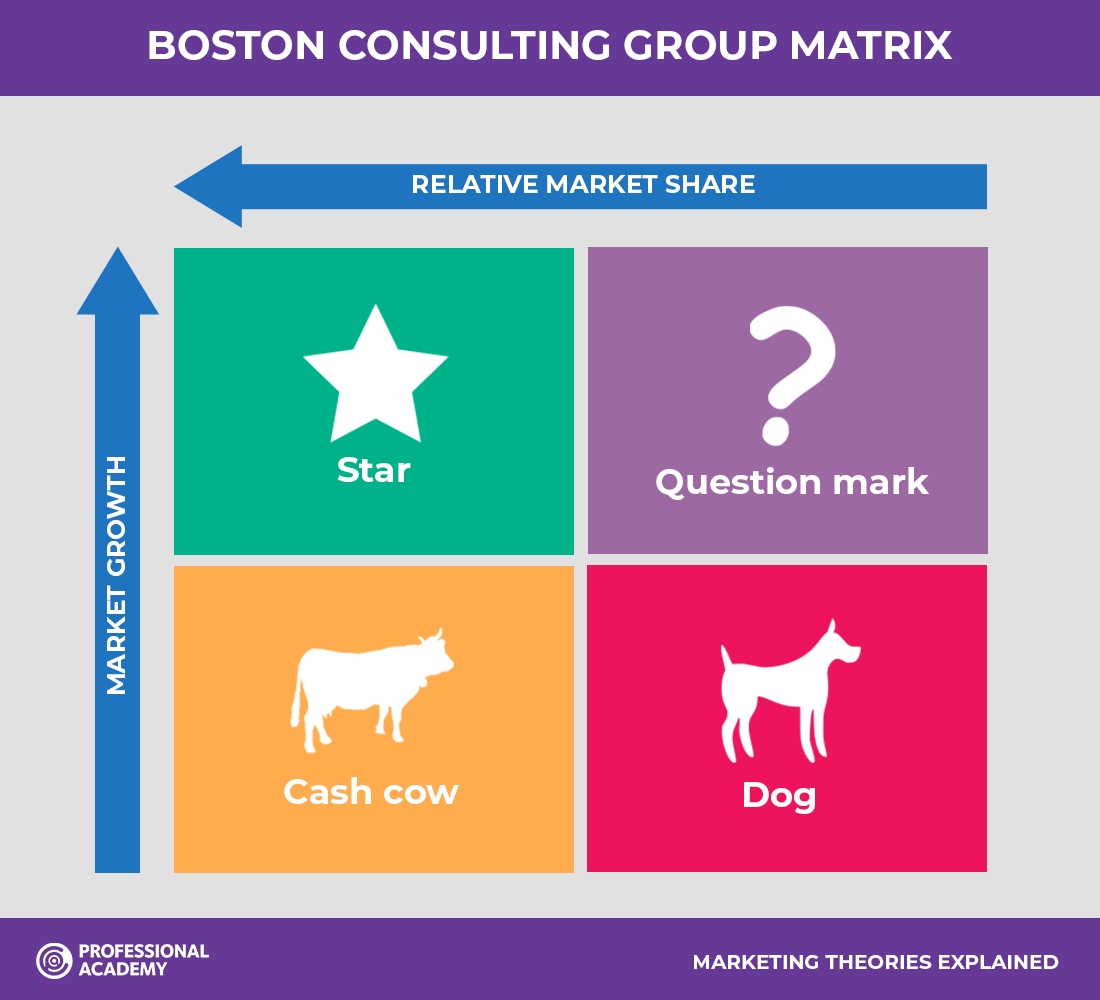
Under different product lines, different types of demands, and even different modules under the same product, in order to maximize the value, the response strategies adopted are different. Then the Boston matrix can be used to judge.
1) Star products
It refers to the product group in the quadrant with high growth rate and high market share. This kind of product may become the cash cow product of the enterprise and needs to increase investment to support its rapid development.
The development strategy adopted is: actively expanding economic scale and market opportunities, aiming at long-term interests, increasing market share and strengthening competitive position. The development strategy and the management and organization of star products are best in the form of business divisions, which are in charge of operators who are proficient in both production technology and sales.
2) Cash cow products
It refers to the product group in the quadrant of low growth rate and high market share, which has entered a mature period.
Its financial characteristics are large sales volume, high product profit margin and low debt ratio, which can provide funds for enterprises, and because of the low growth rate, there is no need to increase investment. As a result, it has become the backing for enterprises to recover funds and support other products, especially the investment of star products.
- Minimize equipment investment and other investments
- Use the oil-pressing method to gain more profits in a short period of time to fund other products
For products whose sales growth rate in this quadrant is still increasing, further market segmentation should be carried out to maintain the existing market growth rate or delay its decline. For cash cow products, it is suitable to use the form of business divisions for management, and its operator is preferably a marketing person.
3) Question marks
It is a product group in the high growth rate, low market share quadrant.
The former shows that the market has great opportunities and good prospects, while the latter shows that there are problems in marketing. Its financial characteristics are low profit margins, insufficient funds, and high debt ratios.
For example, new products that are in the introduction period in the product life cycle and fail to open up the market for various reasons are products with such problems. A selective investment strategy should be adopted for problematic products.
Therefore, the improvement and support schemes for problem products are generally included in the long-term plan of the enterprise; For the management organization of problem products, it is best to adopt the form of think tank or project team, and select people with planning ability, dare to take risks and talents to be responsible.
4) Dog products
It is a product group in the low growth, low market share quadrant. Its financial characteristics are that the profit rate is low, it is in a state of loss, and the debt ratio is high, which cannot bring benefits to the enterprise.
For such products, a withdrawal strategy should be adopted: firstly, the batch should be reduced, gradually withdrawn, and those products with extremely low sales growth rate and market share should be eliminated immediately; secondly, the remaining resources should be transferred to other products; thirdly, the products should be rectified, it is best to combine the thin dog products with other business divisions and manage them in a unified manner.
For different product types, we should use different ways to align with the product strategy.
Finally, if the demands are stipulated in the contract, then these analyses can be skipped and the work can be done according to the contract.
4. The overall process
The above provides a general overview of the demands, most of the methods are mainly integrated in the flow chart, summarized as follows:

If you like the article, please share it with others with page link, thanks for your supporting! ❤


































Leave a comment